
Top ▲

GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Not curated in GtoImmuPdb
Target id: 380
Nomenclature: KCa1.1
Family: Calcium- and sodium-activated potassium channels (KCa, KNa)
Annotation status:
 Annotated and reviewed, awaiting update
» Email us
Annotated and reviewed, awaiting update
» Email us
Gene and Protein Information  |
|||||||
| Species | TM | P Loops | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 1 | 1236 | 10q22.3 | KCNMA1 | potassium calcium-activated channel subfamily M alpha 1 | 44 |
| Mouse | 7 | 1 | 1209 | 14 A3 | Kcnma1 | potassium large conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily M, alpha member 1 | |
| Rat | 7 | 1 | 1209 | 15p16 | Kcnma1 | potassium calcium-activated channel subfamily M alpha 1 | |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | Q12791 (Hs), Q08460 (Mm), Q62976 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL4304 (Hs), CHEMBL2800 (Mm), CHEMBL5505 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | Q12791 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000156113 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000063142 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000005985 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 3778 (Hs), 16531 (Mm), 83731 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000156113 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:3778 (Hs), mmu:16531 (Mm), rno:83731 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 600150 (Hs) |
| Orphanet | ORPHA122795 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q12791 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_001014797 (Hs), NM_010610 (Mm), NM_031828 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_001014797 (Hs), NP_034740 (Mm), NP_114016 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | Q12791 (Hs), Q08460 (Mm), Q62976 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | KCNMA1 (Hs) |
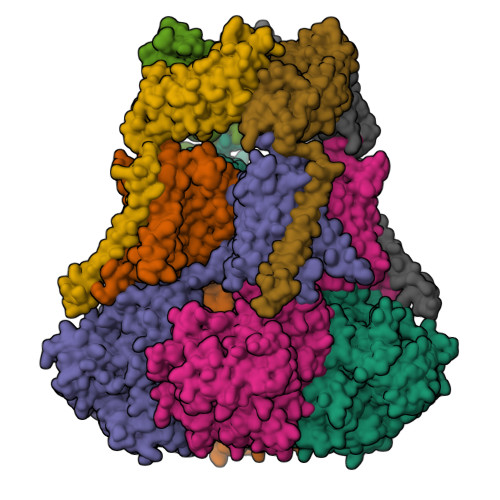
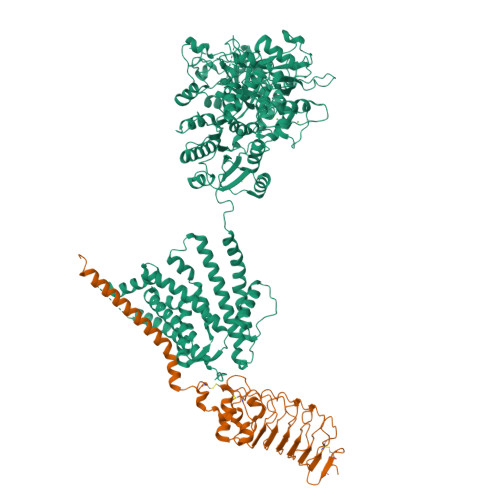
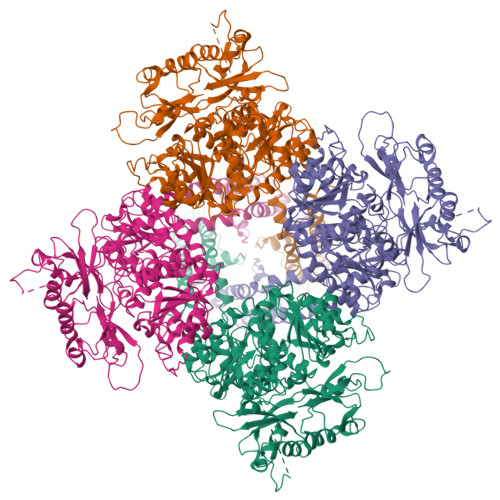
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||
Associated Proteins  |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Functional Characteristics  |
|
| Maxi KCa | |
Ion Selectivity and Conductance  |
||||||
|
||||||
|
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Activators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific activator tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Activator Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mg2+ has also been reported as an activator for the KCa1.1 Progesterone activates channels through binding β1/β4 auxiliary subunits (EC50 ~1-2 μM) [29]. 17β-estradiol and tamoxifen activate channels with β1 auxiliary subunits (EC50 1-10 μM) [10]. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blockers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific channel blocker tables | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blocker Comments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Venom-derived conopeptide Vt3.1 acts as a potassiun channel blocker that preferentially blocks channels with β4 auxiliary subunits (IC50 8.5 μM) [22]. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| General Comments |
|
Channel openers may have applications in stroke, epilepsy, bladder over-reactivity, asthma, hypertension, gastric hypermotility and psychoses [8,16,20]. Crystal Structures have been solved for the Intracellular Gating Rings [54,59-60]. A gene therapy plasmid vector that expresses human KCa1.1 (URO-902) is in clinical development as a novel therapeutic approach for the treament of overactive bladder syndrome associated with detrusor overactivity [11,35]. URO-902 is delivered either by a single intravesical instillation or by direct injections into bladder detrusor muscle, thus limting effects to bladder tissue. |
1. Agarwal S, Kim ED, Lee S, Simon A, Accardi A, Nimigean CM. (2025) Ball-and-chain inactivation of a human large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel. Nat Commun, 16 (1): 1769. [PMID:39971906]
2. Amrutkar DVm Foster K, Jacobsen TA, Jefson MR, Keaney GF, Larsen JS, Nielsen KS. (2018) Potassium channel modulators. Patent number: US9975886B1. Assignee: Cadent Therapeutics Inc. Priority date: 23/01/2018. Publication date: 22/04/2018.
3. Asano S, Bratz IN, Berwick ZC, Fancher IS, Tune JD, Dick GM. (2012) Penitrem A as a tool for understanding the role of large conductance Ca(2+)/voltage-sensitive K(+) channels in vascular function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 342 (2): 453-60. [PMID:22580348]
4. Bentzen BH, Nardi A, Calloe K, Madsen LS, Olesen SP, Grunnet M. (2007) The small molecule NS11021 is a potent and specific activator of Ca2+-activated big-conductance K+ channels. Mol Pharmacol, 72 (4): 1033-44. [PMID:17636045]
5. Blanc E, Romi-Lebrun R, Bornet O, Nakajima T, Darbon H. (1998) Solution structure of two new toxins from the venom of the Chinese scorpion Buthus martensi Karsch blockers of potassium channels. Biochemistry, 37 (36): 12412-8. [PMID:9730813]
6. Brenner R, Jegla TJ, Wickenden A, Liu Y, Aldrich RW. (2000) Cloning and functional characterization of novel large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel beta subunits, hKCNMB3 and hKCNMB4. J Biol Chem, 275 (9): 6453-61. [PMID:10692449]
7. Butler A, Tsunoda S, McCobb DP, Wei A, Salkoff L. (1993) mSlo, a complex mouse gene encoding "maxi" calcium-activated potassium channels. Science, 261 (5118): 221-4. [PMID:7687074]
8. Coghlan MJ, Carroll WA, Gopalakrishnan M. (2001) Recent developments in the biology and medicinal chemistry of potassium channel modulators: update from a decade of progress. J Med Chem, 44 (11): 1627-53. [PMID:11356099]
9. Crest M, Jacquet G, Gola M, Zerrouk H, Benslimane A, Rochat H, Mansuelle P, Martin-Eauclaire MF. (1992) Kaliotoxin, a novel peptidyl inhibitor of neuronal BK-type Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels characterized from Androctonus mauretanicus mauretanicus venom. J Biol Chem, 267 (3): 1640-7. [PMID:1730708]
10. Dick GM, Rossow CF, Smirnov S, Horowitz B, Sanders KM. (2001) Tamoxifen activates smooth muscle BK channels through the regulatory beta 1 subunit. J Biol Chem, 276 (37): 34594-9. [PMID:11454866]
11. Enemchukwu EA, Kalota S, Robertson K, Ge S, Lu J, Badger H, Mujais S, Peters KM. (2025) Gene Therapy With URO-902 (pVAX/hSlo) for the Treatment of Female Patients With Overactive Bladder and Urge Urinary Incontinence: Safety and Efficacy From a Randomized Phase 2a Trial. J Urol, 213 (4): 417-427. [PMID:39693268]
12. Galvez A, Gimenez-Gallego G, Reuben JP, Roy-Contancin L, Feigenbaum P, Kaczorowski GJ, Garcia ML. (1990) Purification and characterization of a unique, potent, peptidyl probe for the high conductance calcium-activated potassium channel from venom of the scorpion Buthus tamulus. J Biol Chem, 265 (19): 11083-90. [PMID:1694175]
13. Garcia ML, Knaus HG, Munujos P, Slaughter RS, Kaczorowski GJ. (1995) Charybdotoxin and its effects on potassium channels. Am J Physiol, 269 (1 Pt 1): C1-10. [PMID:7543240]
14. Garcia-Valdes J, Zamudio FZ, Toro L, Possani LD, Possan LD. (2001) Slotoxin, alphaKTx1.11, a new scorpion peptide blocker of MaxiK channels that differentiates between alpha and alpha+beta (beta1 or beta4) complexes. FEBS Lett, 505 (3): 369-73. [PMID:11576530]
15. Giangiacomo KM, Kamassah A, Harris G, McManus OB. (1998) Mechanism of maxi-K channel activation by dehydrosoyasaponin-I. J Gen Physiol, 112 (4): 485-501. [PMID:9758866]
16. Gribkoff VK, Starrett Jr JE, Dworetzky SI, Hewawasam P, Boissard CG, Cook DA, Frantz SW, Heman K, Hibbard JR, Huston K et al.. (2001) Targeting acute ischemic stroke with a calcium-sensitive opener of maxi-K potassium channels. Nat Med, 7 (4): 471-7. [PMID:11283675]
17. Jensen BS. (2002) BMS-204352: a potassium channel opener developed for the treatment of stroke. CNS Drug Rev, 8 (4): 353-60. [PMID:12481191]
18. Jiang Z, Wallner M, Meera P, Toro L. (1999) Human and rodent MaxiK channel beta-subunit genes: cloning and characterization. Genomics, 55 (1): 57-67. [PMID:9888999]
19. Joiner WJ, Tang MD, Wang LY, Dworetzky SI, Boissard CG, Gan L, Gribkoff VK, Kaczmarek LK. (1998) Formation of intermediate-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels by interaction of Slack and Slo subunits. Nat Neurosci, 1 (6): 462-9. [PMID:10196543]
20. Kaczorowski GJ, Knaus HG, Leonard RJ, McManus OB, Garcia ML. (1996) High-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels; structure, pharmacology, and function. J Bioenerg Biomembr, 28 (3): 255-67. [PMID:8807400]
21. Lee K, Rowe IC, Ashford ML. (1995) NS 1619 activates BKCa channel activity in rat cortical neurones. Eur J Pharmacol, 280 (2): 215-9. [PMID:7589189]
22. Li M, Chang S, Yang L, Shi J, McFarland K, Yang X, Moller A, Wang C, Zou X, Chi C et al.. (2014) Conopeptide Vt3.1 preferentially inhibits BK potassium channels containing β4 subunits via electrostatic interactions. J Biol Chem, 289 (8): 4735-42. [PMID:24398688]
23. Liu G, Shi J, Yang L, Cao L, Park SM, Cui J, Marx SO. (2004) Assembly of a Ca2+-dependent BK channel signaling complex by binding to beta2 adrenergic receptor. EMBO J, 23 (11): 2196-205. [PMID:15141163]
24. Lucchesi K, Ravindran A, Young H, Moczydlowski E. (1989) Analysis of the blocking activity of charybdotoxin homologs and iodinated derivatives against Ca2+-activated K+ channels. J Membr Biol, 109 (3): 269-81. [PMID:2477548]
25. Marshall DL, Vatanpour H, Harvey AL, Boyot P, Pinkasfeld S, Doljansky Y, Bouet F, Ménez A. (1994) Neuromuscular effects of some potassium channel blocking toxins from the venom of the scorpion Leiurus quinquestriatus hebreus. Toxicon, 32 (11): 1433-43. [PMID:7533951]
26. Meera P, Wallner M, Song M, Toro L. (1997) Large conductance voltage- and calcium-dependent K+ channel, a distinct member of voltage-dependent ion channels with seven N-terminal transmembrane segments (S0-S6), an extracellular N terminus, and an intracellular (S9-S10) C terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94 (25): 14066-71. [PMID:9391153]
27. Molinari EJ, Sullivan JP, Wan Y, Brioni JD, Gopalakrishnan M. (2000) Characterization and modulation of [125I]iberiotoxin-D19Y/Y36F binding in the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Eur J Pharmacol, 388 (2): 155-61. [PMID:10666507]
28. Nausch B, Rode F, Jørgensen S, Nardi A, Korsgaard MP, Hougaard C, Bonev AD, Brown WD, Dyhring T, Strøbæk D et al.. (2014) NS19504: a novel BK channel activator with relaxing effect on bladder smooth muscle spontaneous phasic contractions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 350 (3): 520-30. [PMID:24951278]
29. North KC, Shaw AA, Bukiya AN, Dopico AM. (2023) Progesterone activation of β1-containing BK channels involves two binding sites. Nat Commun, 14 (1): 7248. [PMID:37945687]
30. Novello JC, Arantes EC, Varanda WA, Oliveira B, Giglio JR, Marangoni S. (1999) TsTX-IV, a short chain four-disulfide-bridged neurotoxin from Tityus serrulatus venom which acts on Ca2+-activated K+ channels. Toxicon, 37 (4): 651-60. [PMID:10082164]
31. Olesen SP, Munch E, Moldt P, Drejer J. (1994) Selective activation of Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channels by novel benzimidazolone. Eur J Pharmacol, 251 (1): 53-9. [PMID:8137869]
32. Persohn E, Malherbe P, Richards JG. (1992) Comparative molecular neuroanatomy of cloned GABAA receptor subunits in the rat CNS. J Comp Neurol, 326 (2): 193-216. [PMID:1336019]
33. Romi-Lebrun R, Lebrun B, Martin-Eauclaire MF, Ishiguro M, Escoubas P, Wu FQ, Hisada M, Pongs O, Nakajima T. (1997) Purification, characterization, and synthesis of three novel toxins from the Chinese scorpion Buthus martensi, which act on K+ channels. Biochemistry, 36 (44): 13473-82. [PMID:9354615]
34. Romine JL, Martin SW, Meanwell NA, Gribkoff VK, Boissard CG, Dworetzky SI, Natale J, Moon S, Ortiz A, Yeleswaram S et al.. (2007) 3-[(5-Chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-5-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl ]-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2(3H)-one, BMS-191011: opener of large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated potassium (maxi-K) channels, identification, solubility, and SAR. J Med Chem, 50 (3): 528-42. [PMID:17266205]
35. Rovner E, Chai TC, Jacobs S, Christ G, Andersson KE, Efros M, Nitti V, Davies K, McCullough AR, Melman A. (2020) Evaluating the safety and potential activity of URO-902 (hMaxi-K) gene transfer by intravesical instillation or direct injection into the bladder wall in female participants with idiopathic (non-neurogenic) overactive bladder syndrome and detrusor overactivity from two double-blind, imbalanced, placebo-controlled randomized phase 1 trials. Neurourol Urodyn, 39 (2): 744-753. [PMID:31945197]
36. Roy S, Large RJ, Akande AM, Kshatri A, Webb TI, Domene C, Sergeant GP, McHale NG, Thornbury KD, Hollywood MA. (2014) Development of GoSlo-SR-5-69, a potent activator of large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BK) channels. Eur J Med Chem, 75: 426-37. [PMID:24561672]
37. Sanchez M, McManus OB. (1996) Paxilline inhibition of the alpha-subunit of the high-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel. Neuropharmacology, 35 (7): 963-8. [PMID:8938726]
38. Strøbaek D, Christophersen P, Holm NR, Moldt P, Ahring PK, Johansen TE, Olesen SP. (1996) Modulation of the Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channel, hslo, by the substituted diphenylurea NS 1608, paxilline and internal Ca2+. Neuropharmacology, 35 (7): 903-14. [PMID:8938721]
39. Tao J, Zhou ZL, Wu B, Shi J, Chen XM, Ji YH. (2014) Recombinant expression and functional characterization of martentoxin: a selective inhibitor for BK channel (α + β4). Toxins (Basel), 6 (4): 1419-33. [PMID:24759175]
40. Tao X, MacKinnon R. (2019) Molecular structures of the human Slo1 K+ channel in complex with β4. Elife, 8. [PMID:31815672]
41. Tao X, Zhao C, MacKinnon R. (2023) Membrane protein isolation and structure determination in cell-derived membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 120 (18): e2302325120. [PMID:37098056]
42. Teramoto N, Brading AF, Ito Y. (2003) Multiple effects of mefenamic acid on K(+) currents in smooth muscle cells from pig proximal urethra. Br J Pharmacol, 140 (8): 1341-50. [PMID:14623761]
43. Tonggu L, Wang L. (2022) Structure of the Human BK Ion Channel in Lipid Environment. Membranes (Basel), 12 (8). [PMID:36005673]
44. Tseng-Crank J, Foster CD, Krause JD, Mertz R, Godinot N, DiChiara TJ, Reinhart PH. (1994) Cloning, expression, and distribution of functionally distinct Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel isoforms from human brain. Neuron, 13 (6): 1315-30. [PMID:7993625]
45. Valverde MA, Rojas P, Amigo J, Cosmelli D, Orio P, Bahamonde MI, Mann GE, Vergara C, Latorre R. (1999) Acute activation of Maxi-K channels (hSlo) by estradiol binding to the beta subunit. Science, 285 (5435): 1929-31. [PMID:10489376]
46. Wang G, Lemos JR. (1992) Tetrandrine blocks a slow, large-conductance, Ca(2+)-activated potassium channel besides inhibiting a non-inactivating Ca2+ current in isolated nerve terminals of the rat neurohypophysis. Pflugers Arch, 421 (6): 558-65. [PMID:1331975]
47. Wang J, Shen B, Guo M, Lou X, Duan Y, Cheng XP, Teng M, Niu L, Liu Q, Huang Q et al.. (2005) Blocking effect and crystal structure of natrin toxin, a cysteine-rich secretory protein from Naja atra venom that targets the BKCa channel. Biochemistry, 44 (30): 10145-52. [PMID:16042391]
48. Wang RX, Chai Q, Lu T, Lee HC. (2011) Activation of vascular BK channels by docosahexaenoic acid is dependent on cytochrome P450 epoxygenase activity. Cardiovasc Res, 90 (2): 344-52. [PMID:21187320]
49. Wei A, Solaro C, Lingle C, Salkoff L. (1994) Calcium sensitivity of BK-type KCa channels determined by a separable domain. Neuron, 13 (3): 671-81. [PMID:7917297]
50. Weiger TM, Holmqvist MH, Levitan IB, Clark FT, Sprague S, Huang WJ, Ge P, Wang C, Lawson D, Jurman ME, Glucksmann MA, Silos-Santiago I, DiStefano PS, Curtis R. (2000) A novel nervous system beta subunit that downregulates human large conductance calcium-dependent potassium channels. J Neurosci, 20 (10): 3563-70. [PMID:10804197]
51. Wisden W, Laurie DJ, Monyer H, Seeburg PH. (1992) The distribution of 13 GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. I. Telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon. J Neurosci, 12 (3): 1040-62. [PMID:1312131]
52. Wu SN, Chen CC, Li HF, Lo YK, Chen SA, Chiang HT. (2002) Stimulation of the BK(Ca) channel in cultured smooth muscle cells of human trachea by magnolol. Thorax, 57 (1): 67-74. [PMID:11809993]
53. Wu SN, Li HF, Jan CR, Shen AY. (1999) Inhibition of Ca2+-activated K+ current by clotrimazole in rat anterior pituitary GH3 cells. Neuropharmacology, 38 (7): 979-89. [PMID:10428416]
54. Wu Y, Yang Y, Ye S, Jiang Y. (2010) Structure of the gating ring from the human large-conductance Ca(2+)-gated K(+) channel. Nature, 466 (7304): 393-7. [PMID:20574420]
55. Yamanouchi D, Kasuya G, Nakajo K, Kise Y, Nureki O. (2023) Dual allosteric modulation of voltage and calcium sensitivities of the Slo1-LRRC channel complex. Mol Cell, 83 (24): 4555-4569.e4. [PMID:38035882]
56. Yan J, Aldrich RW. (2010) LRRC26 auxiliary protein allows BK channel activation at resting voltage without calcium. Nature, 466 (7305): 513-6. [PMID:20613726]
57. Yan J, Aldrich RW. (2012) BK potassium channel modulation by leucine-rich repeat-containing proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109 (20): 7917-22. [PMID:22547800]
58. Yao J, Chen X, Li H, Zhou Y, Yao L, Wu G, Chen X, Zhang N, Zhou Z, Xu T et al.. (2005) BmP09, a "long chain" scorpion peptide blocker of BK channels. J Biol Chem, 280 (15): 14819-28. [PMID:15695820]
59. Yuan P, Leonetti MD, Hsiung Y, MacKinnon R. (2012) Open structure of the Ca2+ gating ring in the high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel. Nature, 481 (7379): 94-7. [PMID:22139424]
60. Yuan P, Leonetti MD, Pico AR, Hsiung Y, MacKinnon R. (2010) Structure of the human BK channel Ca2+-activation apparatus at 3.0 A resolution. Science, 329 (5988): 182-6. [PMID:20508092]
61. Zhang G, Xu X, Jia Z, Geng Y, Liang H, Shi J, Marras M, Abella C, Magleby KL, Silva JR et al.. (2022) An allosteric modulator activates BK channels by perturbing coupling between Ca2+ binding and pore opening. Nat Commun, 13 (1): 6784. [PMID:36351900]